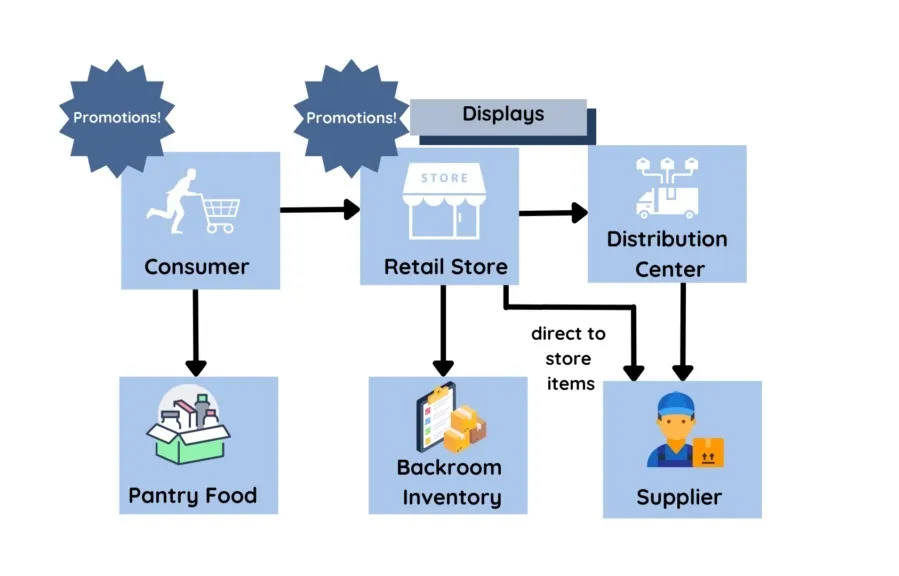
Every retailer has faced this challenge: too much inventory gathering dust on shelves, or too little stock when customers are ready to buy. Both scenarios cost money, damage customer relationships, and create operational headaches.
Retail demand forecasting offers a solution. By predicting future customer demand with accuracy, retailers can optimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and ensure products are available when shoppers need them. This guide breaks down what retail demand forecasting is, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively in your business.
What is Retail Demand Forecasting?
Retail demand forecasting is the process of predicting future customer demand for products based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It helps retailers answer critical questions: How many units of a product should we stock next month? Which items will be popular during the holiday season? When should we mark down slow-moving inventory?
Accurate forecasting enables retailers to make informed decisions about purchasing, pricing, promotions, and staffing. Rather than relying on guesswork, businesses can use data-driven insights to anticipate customer needs and respond proactively.
Why Retail Demand Forecasting Matters
The benefits of effective demand forecasting extend across every aspect of retail operations:
Optimized Inventory Levels: Maintain the right amount of stock without overstocking or understocking. This reduces storage costs and minimizes the risk of markdowns on excess inventory.
Improved Cash Flow: By ordering only what you need, you free up capital that would otherwise be tied up in unsold merchandise.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: When products are consistently available, customers enjoy a better shopping experience and are more likely to return.
Better Supplier Relationships: Accurate forecasts allow you to provide suppliers with reliable order quantities and timelines, strengthening partnerships.
Strategic Planning: Demand forecasting informs decisions about store expansion, product launches, and marketing campaigns.
Key Methods for Retail Demand Forecasting
Retailers use several approaches to forecast demand, each with its own strengths:
Qualitative Forecasting
This method relies on expert judgment, market research, and customer feedback rather than numerical data. It’s particularly useful for new products without historical sales data or when entering unfamiliar markets. However, qualitative forecasting can be subjective and may not scale well for large inventories.
Quantitative Forecasting
Quantitative methods use historical sales data and statistical models to predict future demand. Common techniques include:
- Time Series Analysis: Examines patterns in past sales data to identify trends, seasonality, and cycles
- Regression Analysis: Identifies relationships between demand and variables like price, promotions, or weather
- Moving Averages: Smooths out short-term fluctuations to reveal underlying trends
AI and Machine Learning
Advanced retailers are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms. These technologies can analyze vast datasets, identify complex patterns, and adapt predictions as new information becomes available. Machine learning models can incorporate hundreds of variables simultaneously, from social media sentiment to local events, delivering highly accurate forecasts.
Essential Data for Accurate Forecasting
The quality of your demand forecast depends heavily on the data you feed into it. Prioritize collecting:
- Historical sales data across different time periods
- Inventory levels and stockout incidents
- Promotional calendars and their impact on sales
- Seasonal patterns and cyclical trends
- Economic indicators relevant to your market
- Competitor pricing and promotional activity
- Customer demographics and buying behavior
- External factors like weather, holidays, and local events
Integrate data from multiple sources—point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, customer relationship management tools, and market research—to build a comprehensive picture of demand drivers.
Implementing Retail Demand Forecasting
Start by defining clear objectives. What specific business problems are you trying to solve? Are you focused on reducing stockouts, minimizing excess inventory, or improving service levels?
Next, choose forecasting methods appropriate to your business size, product categories, and available resources. Small retailers might begin with simple moving averages, while larger organizations may invest in sophisticated machine learning platforms.
Establish a regular forecasting cycle—weekly, monthly, or quarterly—depending on your product turnover rates. Fast-moving consumer goods require more frequent updates than durable goods.
Monitor forecast accuracy by comparing predictions against actual sales. Calculate key metrics like mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) to identify areas for improvement. Continuously refine your models based on performance data and changing market conditions.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Data Quality Issues: Incomplete or inaccurate data undermines forecast reliability. Implement robust data governance practices and regularly audit your information sources.
Unexpected Market Changes: External shocks—economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, or viral trends—can render forecasts obsolete. Build flexibility into your planning and maintain safety stock for critical items.
Overreliance on Technology: While algorithms are powerful, they can’t replace human judgment entirely. Combine quantitative forecasts with insights from sales teams, buyers, and category managers who understand nuanced market dynamics.
Siloed Operations: Demand forecasting works best when integrated across departments. Break down barriers between merchandising, supply chain, marketing, and finance to ensure everyone works from the same forecast.
Getting Started with Demand Forecasting
You don’t need a massive budget or complex infrastructure to begin forecasting demand. Start small by analyzing historical sales patterns for your top-selling products. Identify obvious trends and seasonality, then use simple methods like moving averages to project future demand.
As you build confidence and demonstrate value, gradually expand your forecasting efforts to more product categories and incorporate additional data sources. Consider investing in specialized forecasting software that automates calculations and provides visualization tools.
Most importantly, foster a data-driven culture within your organization. Train team members to understand and trust forecasts, and create feedback loops where field observations inform model refinements.
Retail demand forecasting transforms how you manage inventory, serve customers, and grow your business. By predicting future demand with greater accuracy, you reduce costs, improve satisfaction, and position your company for sustainable success.






Leave a Reply